Description
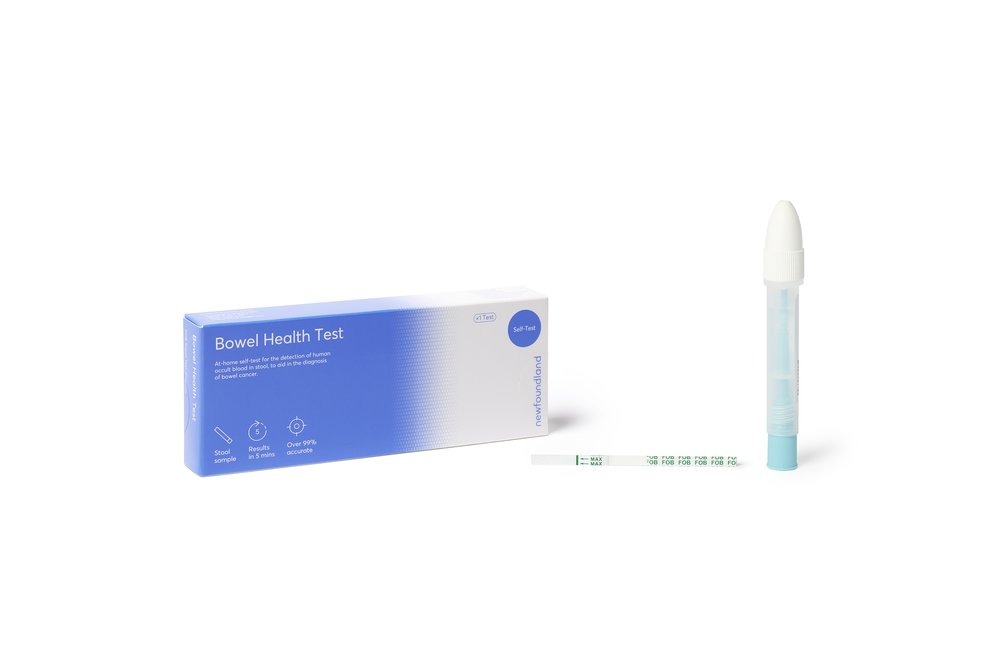
Many diseases can cause hidden blood to appear in the stool. This is also known as fecal occult blood (FOB). In the early stages, gastrointestinal problems such as colorectal cancer, ulcers, polyps, colitis, diverticulitis and fissures may have no visible symptoms, only occult blood. Overall, the lifetime risk of developing colorectal cancer is about 1 in 23 men and 1 in 26 women. Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related death in both men and women, and the second leading cause of cancer-related death when the numbers for men and women are combined. The Newfoundland Bowel Health Test is a rapid fecal immunoassay test (FIT) that can qualitatively detect low levels of fecal occult blood. The test uses a dual antibody assay to selectively detect fecal occult blood. Unlike guaiac assays, the accuracy of the test is not affected by patient diet.
The performance of the test includes:
- Detection limit for FOB - 50 ng/mL
- 99% accuracy
- Result in only 5 minutes
PHZN: 5841508